If You Were a Nurse: Would You Pass This Medical Knowledge Test?
Scroll down to start the test
Anúncios
Imagine you’re on your first hospital shift and a patient’s temperature is being checked. What range would you recognize as a normal adult body temperature?
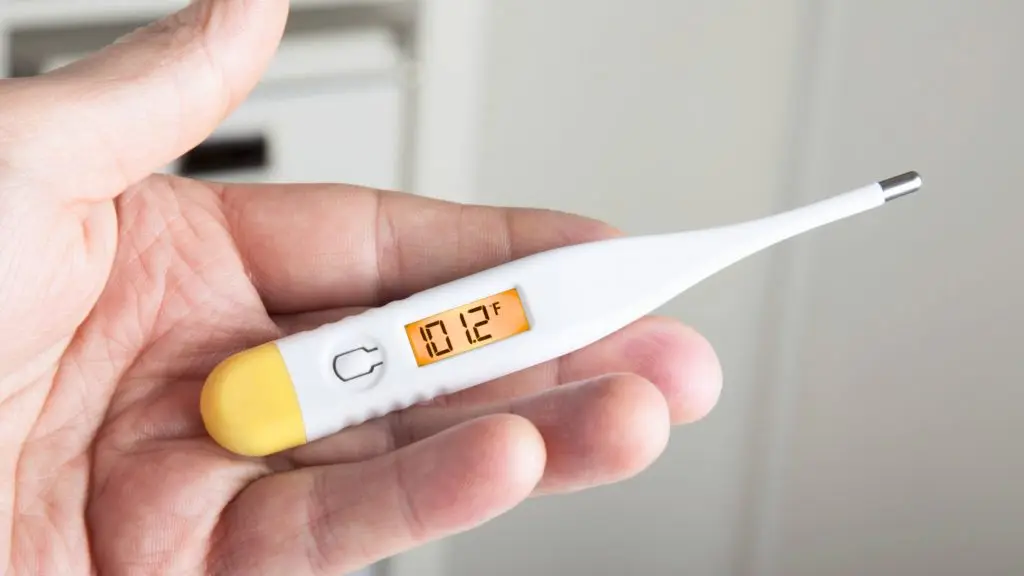
Normal core body temperature is about 37°C. Small individual and daily variations are normal, but 36.5–37.5°C is the typical clinical reference range.
You’re preparing an injection and need to choose the right site. Which is a common intramuscular injection site?

The deltoid is a standard IM site for many vaccines/medications in adults (with proper technique and volume limits). Other common IM sites include vastus lateralis and ventrogluteal.
A patient suddenly collapses and you begin CPR. To keep effective circulation, what compression-to-breath ratio should you follow for an adult?

Current basic life support guidelines for adult CPR recommend 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths (30:2) when performing conventional CPR.
In the ER, you see a patient with severe chest pain. Which condition should you suspect first?

Severe chest pain—especially sudden, crushing pain—should raise immediate suspicion for acute coronary syndrome/MI until proven otherwise; rapid evaluation is essential.
You’re explaining to a patient why handwashing is important. Which of these is the main purpose of proper hand hygiene?

Hand hygiene removes or kills pathogens and is the single most effective measure to prevent healthcare-associated infections and transmission.
It’s the night shift, and a colleague reports a patient’s oxygen saturation is at 82%. How would you classify this?
An SpO₂ of 82% is dangerously low (severe hypoxemia) and typically requires urgent oxygen therapy and evaluation; normal is ~95–100%.
During a blood pressure reading, the systolic value represents:
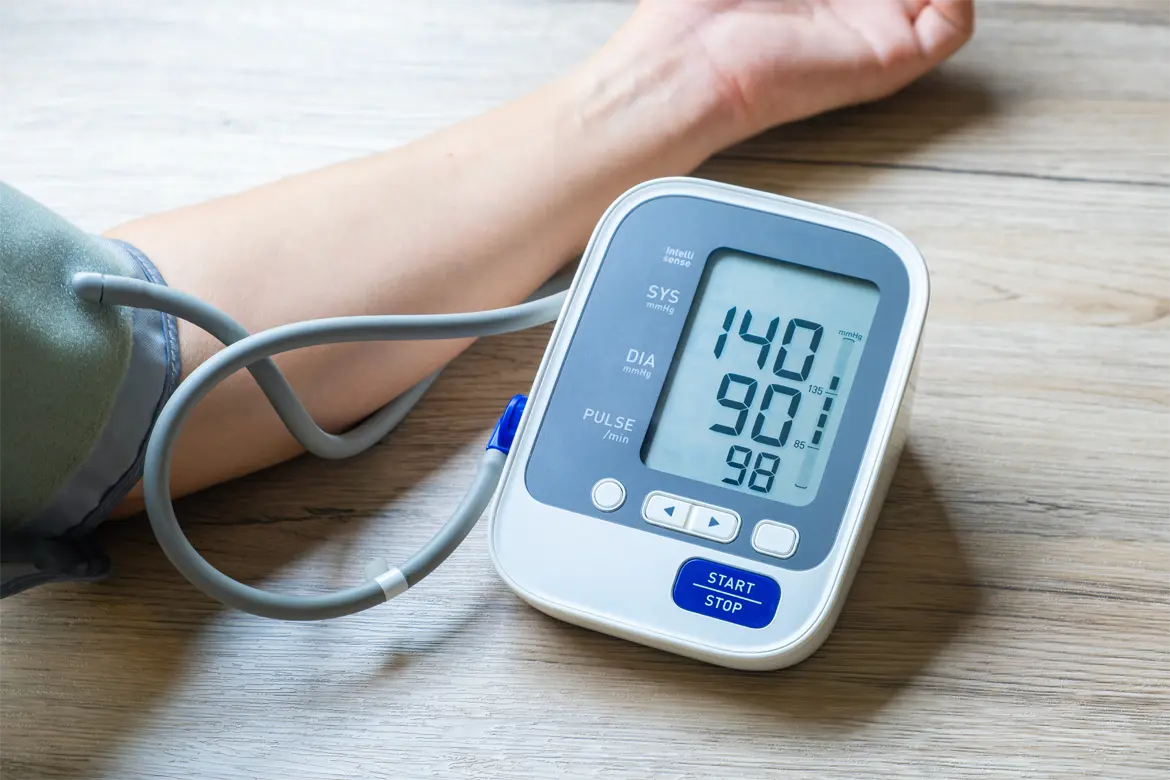
Systolic pressure is the peak arterial pressure during ventricular contraction (systole); diastolic is the pressure during relaxation.
On the ward, a patient is showing signs of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Which of these symptoms would alert you first?
Hypoglycemia often causes adrenergic symptoms like tremor, sweating, palpitations and anxiety (early warning signs). Excessive thirst is more typical of hyperglycemia.
A child arrives with a high fever and stiff neck. Which serious condition should you be alert for?

Fever plus nuchal rigidity (neck stiffness) are classical signs of meningitis, a potentially life-threatening infection requiring urgent assessment and treatment.
During a health education session, someone asks which organ is the largest in the human body. What’s the correct answer?
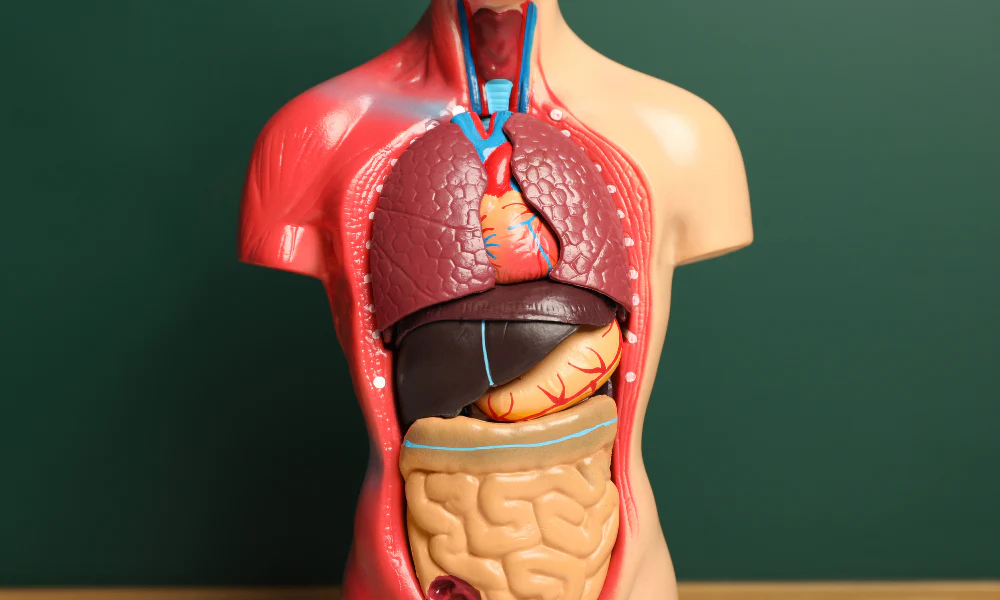
The skin is the largest organ by surface area and weight; it serves as a protective barrier and has many physiological functions.
A patient asks you what their “BMI” means. As a nurse, you explain that BMI stands for:

BMI = Body Mass Index, calculated as weight (kg) ÷ height (m)². It’s a screening tool for underweight/overweight but doesn’t account for muscle vs. fat.
You’re preparing to give medication. The doctor orders it to be administered parenterally. Which route will you choose?
“Parenteral” means routes that bypass the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous). IV is a common parenteral route.
A patient with asthma comes in struggling to breathe. Which type of medication would usually be given first in an emergency?
Acute asthma exacerbations are treated initially with bronchodilators (e.g., short-acting beta-2 agonists) to relieve bronchospasm and improve airflow.
During a routine check-up, you’re recording vital signs. Which of these results would you consider perfectly normal for a healthy adult?

120/80 mmHg is considered a normal blood pressure for adults. A heart rate of 40 is bradycardic, RR of 30 is tachypneic, and SpO₂ of 85% indicates significant hypoxemia.
You’re teaching new students. Which of these is considered the “fifth vital sign”?
Pain assessment is commonly referred to as the “fifth vital sign” because routine evaluation of pain helps guide treatment and improves patient care.
Scroll up to start the test
Welcome to our universe of knowledge and fun! Here, we provide an exciting and interactive experience that invites you to test your knowledge of pop culture, entertainment, history, sports and much more. Our trivia challenges have been meticulously designed to entertain and educate in an engaging and captivating way. We believe that learning can be fun and accessible for everyone. That's why we make it so simple to take part and demonstrate your skills, all from the comfort of your own home.
Anúncios
